5、分布式事务Seata源码学习
本文结合seata的AT模型来对seata的源码实现进行学习
1、Seata的AT模型回顾
1.1、Seata的AT模型
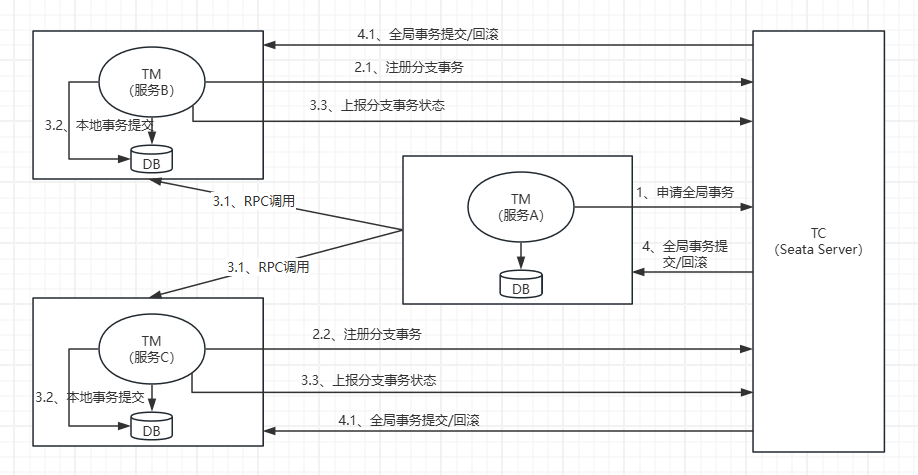
- 在服务A中开启全局事务,向TC申请全局事务id
- 服务A发起RPC远程调用,分布式事务参与方服务B和服务C分别向TC注册分支事务
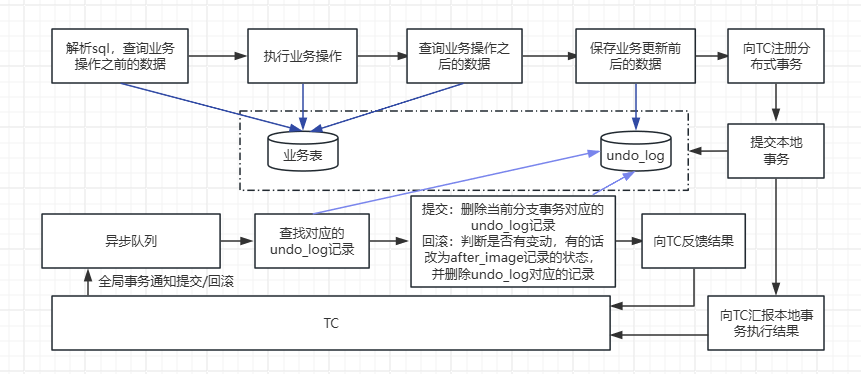
- 参与方提交本地事务,并记录undo_log表
- 参与方上报分支事务的执行状态
- TC根据各分支事务执行状态,通知全局事务是要提交还是回滚
- 分布式事务各参与方TC指示,如果是要提交全局事务,就直接删除本地表的undo_log表里边对应的记录即可,如果是需要回滚,则根据undo_log表里边的before_image对对应的数据进行回滚
1.2、Seata的AT模型在实际开发中的应用
要在应用中使用Seata的AT模型也非常简单,只需要简单几步:
- ① 引入seata依赖
- ② 创建本地undo_log表
- ③ 在配置文件中进行Seata相关的配置
- ④
@GlobalTransactional注解开启分布式事务
具体操作见前面的博客内容
2、核心步骤源码分析(AT)
2.1、RM、TM建立与TC的连接
要想开启分布式事务,前提是RM、TM持有和TC的连接,这样才能完成通信。那么这个连接是在什么时候建立的呢?首先我们看一下@GlobalTransactional注解的包结构:
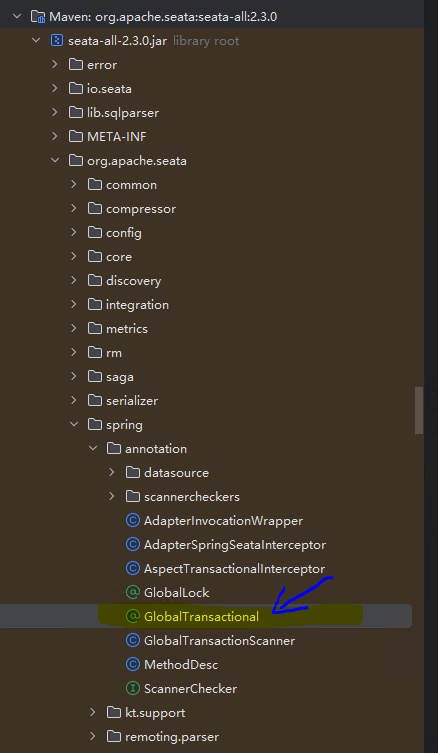
可以看到这个注解定义在org.apache.seata.spring.annotation这个包下,与此同时还定义了一个以Scanner结尾的扫描器,点开看一下这个扫描器
public class GlobalTransactionScanner extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator
implements CachedConfigurationChangeListener, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean {
这个扫描器实现了InitializingBean这个接口,那么就一定实现了它的afterPropertiesSet方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (disableGlobalTransaction) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global transaction is disabled.");
}
ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION, (CachedConfigurationChangeListener) this);
return;
}
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
initClient(); //初始化客户端,什么客户端呢?
}
this.findBusinessBeanNamesNeededEnhancement();
}
这里有一个初始化客户端的方法,那么初始化的是什么客户端呢?继续点进去就可以看到初始化TM和RM的代码
protected void initClient() {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Initializing Global Transaction Clients ... ");
}
if (DEFAULT_TX_GROUP_OLD.equals(txServiceGroup)) {
LOGGER.warn("the default value of seata.tx-service-group: {} has already changed to {} since Seata 1.5, " +
"please change your default configuration as soon as possible " +
"and we don't recommend you to use default tx-service-group's value provided by seata",
DEFAULT_TX_GROUP_OLD, DEFAULT_TX_GROUP);
}
if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(applicationId) || StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(txServiceGroup)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("applicationId: %s, txServiceGroup: %s", applicationId, txServiceGroup));
}
//init TM
TMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup, accessKey, secretKey);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Transaction Manager Client is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
//init RM
RMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Resource Manager is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global Transaction Clients are initialized. ");
}
registerSpringShutdownHook();
}
以初始化RM的代码为例,继续
public class RMClient {
/**
* Init.
*
* @param applicationId the application id
* @param transactionServiceGroup the transaction service group
*/
public static void init(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup) {
RmNettyRemotingClient rmNettyRemotingClient = RmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup);
rmNettyRemotingClient.setResourceManager(DefaultResourceManager.get());
rmNettyRemotingClient.setTransactionMessageHandler(DefaultRMHandler.get());
rmNettyRemotingClient.init();
}
}
继续点进init方法来到org.apache.seata.core.rpc.netty.RmNettyRemotingClient#init
@Override
public void init() {
// registry processor
registerProcessor();
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
super.init();
// Found one or more resources that were registered before initialization
if (resourceManager != null
&& !resourceManager.getManagedResources().isEmpty()
&& StringUtils.isNotBlank(transactionServiceGroup)) {
boolean failFast = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().getBoolean(
ConfigurationKeys.ENABLE_RM_CLIENT_CHANNEL_CHECK_FAIL_FAST,
DefaultValues.DEFAULT_CLIENT_CHANNEL_CHECK_FAIL_FAST);
getClientChannelManager().initReconnect(transactionServiceGroup, failFast);
}
}
}
先看一下super.init(),进入org.apache.seata.core.rpc.netty.AbstractNettyRemotingClient#init
@Override
public void init() {
timerExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
clientChannelManager.reconnect(getTransactionServiceGroup());
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOGGER.warn("reconnect server failed. {}", ex.getMessage());
}
}, SCHEDULE_DELAY_MILLS, SCHEDULE_INTERVAL_MILLS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (this.isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()) {
mergeSendExecutorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),
new NamedThreadFactory(getThreadPrefix(), MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD));
mergeSendExecutorService.submit(new MergedSendRunnable());
}
super.init();
clientBootstrap.start();
}
这里调了一个getTransactionServiceGroup()方法,transactionServiceGroup我们之前就在配置文件中配置过,前面提到会根据这个serviceGroup去找到对应的SeataServer,不妨点clientChannelManager.reconnect() 进去看一下,看是不是根据这个serviceGroup去连接TC,点进去之后经过几个重载的方法后来到了doReconnect方法:
void doReconnect(String transactionServiceGroup, boolean failFast) {
List<String> availList;
try {
availList = getAvailServerList(transactionServiceGroup);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to get available servers: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
throwFailFastException(failFast, "Failed to get available servers");
return;
}
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(availList)) {
RegistryService registryService = RegistryFactory.getInstance();
String clusterName = registryService.getServiceGroup(transactionServiceGroup);
if (StringUtils.isBlank(clusterName)) {
LOGGER.error("can not get cluster name in registry config '{}{}', please make sure registry config correct",
ConfigurationKeys.SERVICE_GROUP_MAPPING_PREFIX,
transactionServiceGroup);
throwFailFastException(failFast, "can not get cluster name in registry config.");
return;
}
if (!(registryService instanceof FileRegistryServiceImpl)) {
LOGGER.error("no available service found in cluster '{}', please make sure registry config correct and keep your seata server running", clusterName);
}
throwFailFastException(failFast, "no available service found in cluster.");
return;
}
try {
doReconnect(availList, transactionServiceGroup);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (failFast) {
throw e;
}
LOGGER.error("connect server failed. {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
确实是拿到了一个可用的地址列表availList,然后根据这个列表继续调了doReconnect方法
void doReconnect(List<String> availList, String transactionServiceGroup) {
Set<String> channelAddress = new HashSet<>(availList.size());
Map<String, Exception> failedMap = new HashMap<>();
try {
for (String serverAddress : availList) {
try {
acquireChannel(serverAddress);
channelAddress.add(serverAddress);
} catch (Exception e) {
failedMap.put(serverAddress, e);
}
}
if (failedMap.size() > 0) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.error("{} can not connect to {} cause:{}", FrameworkErrorCode.NetConnect.getErrCode(),
failedMap.keySet(),
failedMap.values().stream().map(Throwable::getMessage).collect(Collectors.toSet()));
} else if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
failedMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
LOGGER.error("{} can not connect to {} cause:{} trace information:",
FrameworkErrorCode.NetConnect.getErrCode(), key, value.getMessage(), value);
});
}
}
if (availList.size() == failedMap.size()) {
String invalidAddress = StringUtils.join(failedMap.keySet().iterator(), ", ");
throw new FrameworkException("can not connect to [" + invalidAddress + "]");
}
} finally {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(channelAddress)) {
List<InetSocketAddress> aliveAddress = new ArrayList<>(channelAddress.size());
for (String address : channelAddress) {
String[] array = NetUtil.splitIPPortStr(address);
aliveAddress.add(new InetSocketAddress(array[0], Integer.parseInt(array[1])));
}
RegistryFactory.getInstance().refreshAliveLookup(transactionServiceGroup, aliveAddress);
} else {
RegistryFactory.getInstance().refreshAliveLookup(transactionServiceGroup, Collections.emptyList());
}
}
}
可以看到会根据这个列表迭代,然后根据每个serverAddress通过acquireChannel方法获取了一个Channel(如果没有现成的连接,则会通过doConnect(serverAddress)方法创建一个channel)
Channel acquireChannel(String serverAddress) {
Channel channelToServer = channels.get(serverAddress);
if (channelToServer != null) {
channelToServer = getExistAliveChannel(channelToServer, serverAddress);
if (channelToServer != null) {
return channelToServer;
}
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("will connect to {}", serverAddress);
}
Object lockObj = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(channelLocks, serverAddress, key -> new Object());
synchronized (lockObj) {
return doConnect(serverAddress);
}
}
TM的连接建立流程类似,总的来说大致的流程如下:
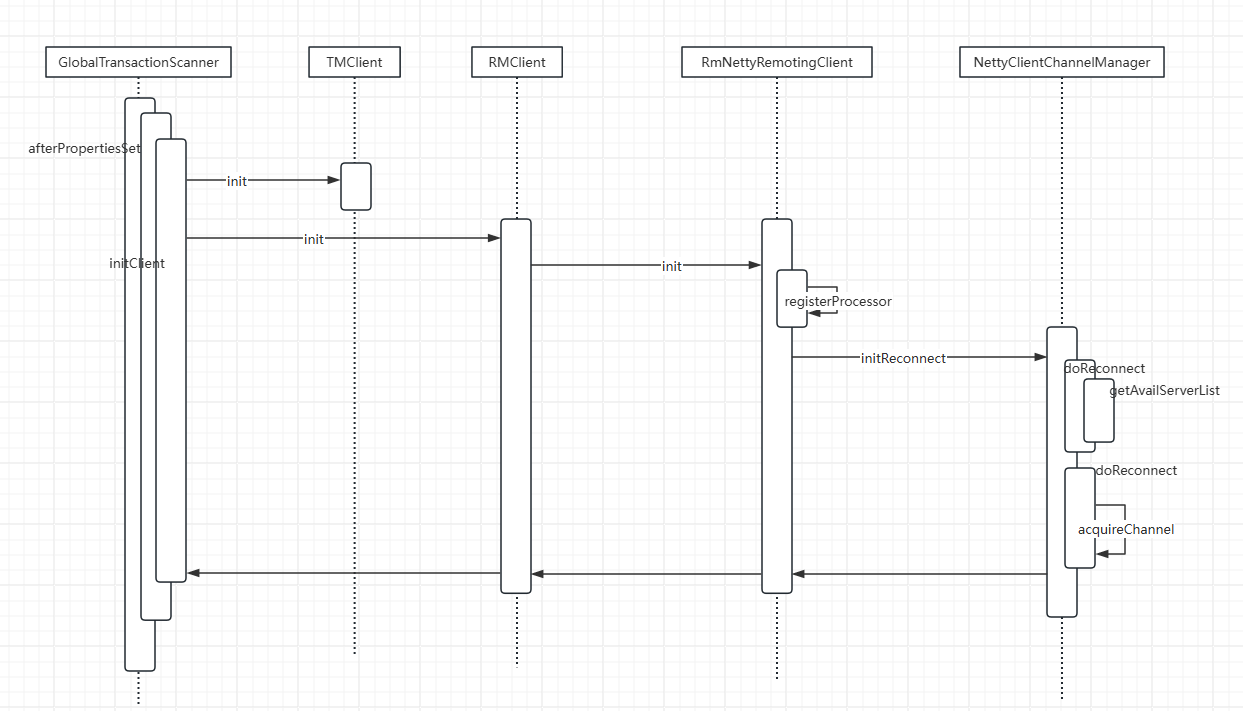
2.2、事务处理
前面我们知道,分布式事务的开启是靠@GlobalTransactional这个注解开启的,那么肯定就有一个地方来识别这个注解并做一些事情。如果是我们自己来做的化,最先想到的肯定是基于aop来做,而从最上面的那个包结构截图可以看到,紧挨着GlobalTransactional这个注解还定义了一个AspectTransactionalInterceptor类
public class AspectTransactionalInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
既然这个类实现了MethodInterceptor接口,那程序在执行的时候肯定会调用它的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
InvocationWrapper invocationWrapper = new DefaultInvocationWrapper(null, invocation.getThis(), specificMethod, invocation.getArguments());
return this.globalTransactionalInterceptorHandler.invoke(invocationWrapper);
}
继续点进去最后一行的globalTransactionalInterceptorHandler.invoke方法,就来到了org.apache.seata.integration.tx.api.interceptor.handler.AbstractProxyInvocationHandler#invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(InvocationWrapper invocation) throws Throwable {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(getMethodsToProxy()) && !getMethodsToProxy().contains(invocation.getMethod().getName())) {
return invocation.proceed();
}
if (nextInvocationHandlerChain != null) {
invocation = new NestInterceptorHandlerWrapper(nextInvocationHandlerChain, ihttp://blog.shengxiao.tech/imagesnvocation);
}
return doInvoke(invocation);
}
最终来到org.apache.seata.integration.tx.api.interceptor.handler.GlobalTransactionalInterceptorHandler#doInvoke
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(InvocationWrapper invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = invocation.getTarget().getClass();
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
boolean localDisable = disable || (ATOMIC_DEGRADE_CHECK.get() && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
final AspectTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation = getAspectTransactional(specificMethod, targetClass);
final GlobalLockConfig globalLockAnnotation = getGlobalLockConfig(specificMethod, targetClass);
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null || this.aspectTransactional != null) {
AspectTransactional transactional;
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {
transactional = globalTransactionalAnnotation;
} else {
transactional = this.aspectTransactional;
}
return handleGlobalTransaction(invocation, transactional);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
return handleGlobalLock(invocation, globalLockAnnotation);
}
}
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
这里边有两个分支,一个是如果globalTransactionalAnnotation或者aspectTransactional不是空的话,就进入handleGlobalTransaction,否则进入handleGlobalLock
进入org.apache.seata.integration.tx.api.interceptor.handler.GlobalTransactionalInterceptorHandler#handleGlobalTransaction,其实只有一行transactionalTemplate.execute,但是这个方法的调用传了一个匿名内部类进来,看一下这个execute方法
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. Get transactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 Handle the transaction propagation.
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
switch (propagation) {
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend(false);
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend(false);
}
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// If current transaction is existing, execute with current transaction,else create
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrentOrCreate();
break;
case NEVER:
// If transaction is existing, throw exception.
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// set current tx config to holder
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
if (tx.getGlobalTransactionRole() == GlobalTransactionRole.Participant) {
LOGGER.info("join into a existing global transaction,xid={}", tx.getXid());
}
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// Do Your Business
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
commitTransaction(tx, txInfo);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
triggerAfterCompletion(tx);
cleanUp(tx);
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}
这里看到两个重点内容:
- 事务传播属性
seata自己定义了几种事务传播属性,但基本上保持和spring的事务传播属性定义一致,比如NOT_SUPPORTED的时候,将当前事务挂起,以非事务的方式执行并返回;再比如REQUIRES_NEW的时候,将当前事务挂起,然后创建一个新的事务并继续执行后续的事务和业务逻辑。
这里一共定义了6种,相比较spring少了一种
NESTED:
- NOT_SUPPORTED:不支持事务,如果有事务,则挂起,以非事务的方式运行
- REQUIRES_NEW:如果当前有事务,则将当前事务挂起,然后新起一个事务执行
- SUPPORTS:如果当前没有事务,则以非事务的方式执行,否则就以当前事务执行
- REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,则创建一个事务执行,否则就用当前事务执行
- NEVER:如果当前存在事务,则报错,如果不存在事务,就正常按照非事务的方式执行
- MANDATORY:如果当前事务不存在,则报错,如果存在,就以当前事务执行
- 事务的处理
上面的代码可以明显看到beginTransaction、c、commitTransaction、以及最里边的catch里边的completeTransactionAfterThrowing
1、beginTransaction方法
private void beginTransaction(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException { if (tx.getGlobalTransactionRole() != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) { if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Ignore begin: just involved in global transaction [{}]", tx.getXid()); } return; } try { triggerBeforeBegin(); tx.begin(txInfo.getTimeOut(), txInfo.getName()); triggerAfterBegin(); } catch (TransactionException txe) { throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe, TransactionalExecutor.Code.BeginFailure); } }这个方法里边就是触发事务开启之前、事务开启、以及触发开启事务之后三个方法,主要看下tx.begin
org.apache.seata.tm.api.DefaultGlobalTransaction#begin(int, java.lang.String)@Override public void begin(int timeout, String name) throws TransactionException { this.createTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (role != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) { assertXIDNotNull(); if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Ignore Begin(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid); } return; } assertXIDNull(); String currentXid = RootContext.getXID(); if (currentXid != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Global transaction already exists," + " can't begin a new global transaction, currentXid = " + currentXid); } xid = transactionManager.begin(null, null, name, timeout); status = GlobalStatus.Begin; RootContext.bind(xid); if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) { LOGGER.info("Begin new global transaction [{}]", xid); } }这个方法开启了一个事务,并且得到一个xid,然后将这个xid绑定到上下文中,具体怎么开启的事务呢?其实就是执行一个远程调用
org.apache.seata.tm.DefaultTransactionManager#begin@Override public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout) throws TransactionException { GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest(); request.setTransactionName(name); request.setTimeout(timeout); GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request); if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) { throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg()); } return response.getXid(); }也就是这里的
syncCall,会得到一个响应public class GlobalBeginResponse extends AbstractTransactionResponse { private String xid; private String extraData; }2、commitTransaction
这个方法是提交事务的方法,方法里边如果超时,会回滚;如果正常提交,会在提交之前触发提交前的hook,在提交之后触发提交后的hook
private void commitTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx, TransactionInfo txInfo) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException, TransactionException { if (tx.getGlobalTransactionRole() != GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher) { if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Ignore commit: just involved in global transaction [{}]", tx.getXid()); } return; } if (isTimeout(tx.getCreateTime(), txInfo)) { // business execution timeout Exception exx = new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.TransactionTimeout, String.format("client detected transaction timeout before commit, so change to rollback, xid = %s", tx.getXid())); rollbackTransaction(tx, exx); return; } try { triggerBeforeCommit(); tx.commit(); GlobalStatus afterCommitStatus = tx.getLocalStatus(); TransactionalExecutor.Code code = TransactionalExecutor.Code.Unknown; switch (afterCommitStatus) { case TimeoutRollbacking: code = TransactionalExecutor.Code.Rollbacking; break; case TimeoutRollbacked: code = TransactionalExecutor.Code.RollbackDone; break; case Finished: code = TransactionalExecutor.Code.CommitFailure; break; default: } Exception statusException = null; if (GlobalStatus.isTwoPhaseHeuristic(afterCommitStatus)) { statusException = new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.CommitHeuristic, String.format("Global transaction[%s] not found, may be rollbacked.", tx.getXid())); } else if (GlobalStatus.isOnePhaseTimeout(afterCommitStatus)) { statusException = new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.TransactionTimeout, String.format("Global transaction[%s] is timeout and will be rollback[TC].", tx.getXid())); } if (null != statusException) { throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, statusException, code); } triggerAfterCommit(); } catch (TransactionException txe) { // 4.1 Failed to commit throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe, TransactionalExecutor.Code.CommitFailure); } }3、completeTransactionAfterThrowing
这个方法在catch里边,也就是说当程序执行异常的时候会执行。点进去看到里边会进行事务的回滚(事务信息不为空 且 抛出的异常是指定的事务回滚异常)
private void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(TransactionInfo txInfo, GlobalTransaction tx, Throwable originalException) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException, TransactionException { //roll back if (txInfo != null && txInfo.rollbackOn(originalException)) { rollbackTransaction(tx, originalException); } else { // not roll back on this exception, so commit commitTransaction(tx, txInfo); } }4、business.execute
执行的业务方法
2.3、各事务角色的请求交互
前面看到事务的”拆解“执行过程,那么RM/TM与RC之间是如何交互的呢?总的来说有异步和同步的方式。下面以开启事务方法org.apache.seata.tm.DefaultTransactionManager#begin为例
@Override
public String begin(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String name, int timeout)
throws TransactionException {
GlobalBeginRequest request = new GlobalBeginRequest();
request.setTransactionName(name);
request.setTimeout(timeout);
GlobalBeginResponse response = (GlobalBeginResponse) syncCall(request);
if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BeginFailed, response.getMsg());
}
return response.getXid();
}
继续看syncCall方法
private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
try {
return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
}
}
继续org.apache.seata.core.rpc.netty.AbstractNettyRemotingClient#sendSyncRequest(java.lang.Object)方法
@Override
public Object sendSyncRequest(Object msg) throws TimeoutException {
String serverAddress = loadBalance(getTransactionServiceGroup(), msg);
long timeoutMillis = this.getRpcRequestTimeout();
RpcMessage rpcMessage = buildRequestMessage(msg, ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_RESQUEST_SYNC);
// send batch message
// put message into basketMap, @see MergedSendRunnable
if (this.isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()) {
// send batch message is sync request, needs to create messageFuture and put it in futures.
MessageFuture messageFuture = new MessageFuture();
messageFuture.setRequestMessage(rpcMessage);
messageFuture.setTimeout(timeoutMillis);
futures.put(rpcMessage.getId(), messageFuture);
// put message into basketMap
BlockingQueue<RpcMessage> basket = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(basketMap, serverAddress,
key -> new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
if (!basket.offer(rpcMessage)) {
LOGGER.error("put message into basketMap offer failed, serverAddress:{},rpcMessage:{}",
serverAddress, rpcMessage);
return null;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("offer message: {}", rpcMessage.getBody());
}
if (!isSending) {
synchronized (mergeLock) {
mergeLock.notifyAll();
}
}
try {
Object response = messageFuture.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return response;
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("wait response error:{},ip:{},request:{}", exx.getMessage(), serverAddress, rpcMessage.getBody());
if (exx instanceof TimeoutException) {
throw (TimeoutException)exx;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
} else {
Channel channel = clientChannelManager.acquireChannel(serverAddress);
return super.sendSync(channel, rpcMessage, timeoutMillis);
}
}
在这个方法里边,外边的if分支逻辑为如果开启了批量提交请求,则走if,否则,就同步调用else里边的逻辑。而在if这个逻辑里边seata的方案是将请求封装成一个org.apache.seata.core.protocol.RpcMessage对象,然后将其丢到一个阻塞队列里边,交由定时异步任务去消费处理。这个阻塞队列又以serverAddress作为key放到了一个map里边。异步任务真正获取数据是从这个map里边获取的。
这个basketMap在哪儿消费处理呢?
前面我们在看RM、TM建立与TC连接的代码的时候就看到了org.apache.seata.core.rpc.netty.AbstractNettyRemotingClient#init
@Override
public void init() {
timerExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
clientChannelManager.reconnect(getTransactionServiceGroup());
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOGGER.warn("reconnect server failed. {}", ex.getMessage());
}
}, SCHEDULE_DELAY_MILLS, SCHEDULE_INTERVAL_MILLS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (this.isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()) {
mergeSendExecutorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),
new NamedThreadFactory(getThreadPrefix(), MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD));
mergeSendExecutorService.submit(new MergedSendRunnable());
}
super.init();
clientBootstrap.start();
}
这里一个将一个MergedSendRunnable的任务丢到了线程池中去交由线程池调度执行。这个类的run方法如下:
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (mergeLock) {
try {
mergeLock.wait(MAX_MERGE_SEND_MILLS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
isSending = true;
basketMap.forEach((address, basket) -> {
if (basket.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
MergedWarpMessage mergeMessage = new MergedWarpMessage();
while (!basket.isEmpty()) {
RpcMessage msg = basket.poll();
mergeMessage.msgs.add((AbstractMessage) msg.getBody());
mergeMessage.msgIds.add(msg.getId());
}
if (mergeMessage.msgIds.size() > 1) {
printMergeMessageLog(mergeMessage);
}
Channel sendChannel = null;
try {
// send batch message is sync request, but there is no need to get the return value.
// Since the messageFuture has been created before the message is placed in basketMap,
// the return value will be obtained in ClientOnResponseProcessor.
sendChannel = clientChannelManager.acquireChannel(address);
AbstractNettyRemotingClient.this.sendAsyncRequest(sendChannel, mergeMessage);
} catch (FrameworkException e) {
if (e.getErrcode() == FrameworkErrorCode.ChannelIsNotWritable && sendChannel != null) {
destroyChannel(address, sendChannel);
}
// fast fail
for (Integer msgId : mergeMessage.msgIds) {
MessageFuture messageFuture = futures.remove(msgId);
Integer parentId = childToParentMap.remove(msgId);
if (parentId != null) {
mergeMsgMap.remove(parentId);
}
if (messageFuture != null) {
messageFuture.setResultMessage(
new RuntimeException(String.format("%s is unreachable", address), e));
}
}
LOGGER.error("client merge call failed: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
});
isSending = false;
}
}
这个任务类的run方法的try里边就是真正发送请求的方法AbstractNettyRemotingClient.this.sendAsyncRequest(sendChannel, mergeMessage);
@Override
public void sendAsyncRequest(Channel channel, Object msg) {
if (channel == null) {
LOGGER.warn("sendAsyncRequest nothing, caused by null channel.");
return;
}
RpcMessage rpcMessage = buildRequestMessage(msg, msg instanceof HeartbeatMessage
? ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_HEARTBEAT_REQUEST
: ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_RESQUEST_ONEWAY);
Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
if (body instanceof MergeMessage) {
Integer parentId = rpcMessage.getId();
mergeMsgMap.put(parentId, (MergeMessage)rpcMessage.getBody());
if (body instanceof MergedWarpMessage) {
for (Integer msgId : ((MergedWarpMessage)rpcMessage.getBody()).msgIds) {
childToParentMap.put(msgId, parentId);
}
}
}
super.sendAsync(channel, rpcMessage);
}

